이 글은 PyTorch 공식 블로그의 글을 번역한 것입니다. 번역 글은 원문을 함께 표시합니다. 원문을 읽으시려면 여기를 클릭하세요. (This article is a Korean translation of the original post on the PyTorch official blog. Below translation includes the original text. To read the original post, click here.)
개요 / Overview
INT8 양자화(quantization)는 x86 CPU 플랫폼에서 딥러닝 추론 속도를 높이는 강력한 기법입니다. 모델의 가중치와 활성화의 정밀도를 32비트 부동소수점(FP32; 32-bit floating-point)에서 8비트 정수(INT8; 8-bit integer)로 줄임으로써 INT8 양자화는 정확도를 유지하면서도 추론 속도와 메모리 요구량을 크게 향상시킬 수 있었습니다.
INT8 quantization is a powerful technique for speeding up deep learning inference on x86 CPU platforms. By reducing the precision of the model’s weights and activations from 32-bit floating-point (FP32) to 8-bit integer (INT8), INT8 quantization can significantly improve the inference speed and reduce memory requirements without sacrificing accuracy.
이번 글에서는 파이토치(PyTorch)에서 x86 CPU용 INT8 양자화의 발전 상황에 대해서 논의해보겠습니다. 주로 새로운 x86 양자화 백엔드(quantization backend)에 초점을 맞추고, 파이토치 2.0 익스포트(PT2E; PyTorch 2.0 Export)와 TorchInductor(토치인덕터)를 사용한 새로운 양자화 경로에 대해서도 간략히 살펴보겠습니다.
In this blog, we will discuss the recent progress on INT8 quantization for x86 CPU in PyTorch, focusing on the new x86 quantization backend. We will also briefly look at the new quantization path with PyTorch 2.0 Export (PT2E) and TorchInductor.
X86 양자화 백엔드 / X86 Quantization Backend
현재 파이토치(PyTorch)에서 권장하는 양자화 방법은 FX입니다. PyTorch 2.0 이전에는 x86 CPU의 기본 양자화 백엔드(일명 QEngine)는 FBGEMM(FB+GEMM; Facebook GEneral Matrix Multiplication)으로, 성능 향상을 위해 FBGEMM 라이브러리를 활용했습니다. PyTorch 2.0 출시 시에는 FBGEMM을 대체하기 위해 X86이라는 새로운 양자화 백엔드가 도입되었습니다. x86 양자화 백엔드는 FBGEMM과 인텔(Intel)® oneDNN (oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library) 커널 라이브러리의 강점을 모두 활용하여, 기존 FBGEMM 백엔드에 비해 향상된 INT8 추론 성능을 제공합니다.
The current recommended way of quantization in PyTorch is FX. Before PyTorch 2.0, the default quantization backend (a.k.a. QEngine) on x86 CPUs was FBGEMM, which leveraged the FBGEMM performance library to achieve the performance speedup. In the PyTorch 2.0 release, a new quantization backend called X86 was introduced to replace FBGEMM. The x86 quantization backend offers improved INT8 inference performance when compared to the original FBGEMM backend by leveraging the strengths of both FBGEMM and the Intel® oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) kernel libraries.
X86 백엔드의 성능 향상 / Performance Benefit from X86 Backend
새로운 X86 백엔드의 성능 향상을 측정하기 위해, 4세대 인텔(Intel)® 제온(Xeon)® 스케일러블 프로세서를 사용하여 인기있는 69종의 딥러닝 모델(아래 그림 1 ~ 그림 3 참조)에 대해 INT8 추론을 실행했습니다. 그 결과, FP32 추론 성능에 비해 2.97배의 기하평균(geomean) 성능 속도 향상을 보였으며, FBGEMM 백엔드에서는 1.43배의 속도 향상을 보였습니다. 아래 차트는 x86 백엔드와 FBGEMM 백엔드를 비교한 모델별 성능 속도 향상을 보여줍니다.
To measure the performance benefits of the new X86 backend, we ran INT8 inference on 69 popular deep learning models (shown in Figures 1-3 below) using 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors. The results showed a 2.97X geomean performance speedup compared to FP32 inference performance, while the speedup was 1.43X with the FBGEMM backend. The charts below show the per-model performance speedup comparing the x86 backend and the FBGEMM backend.
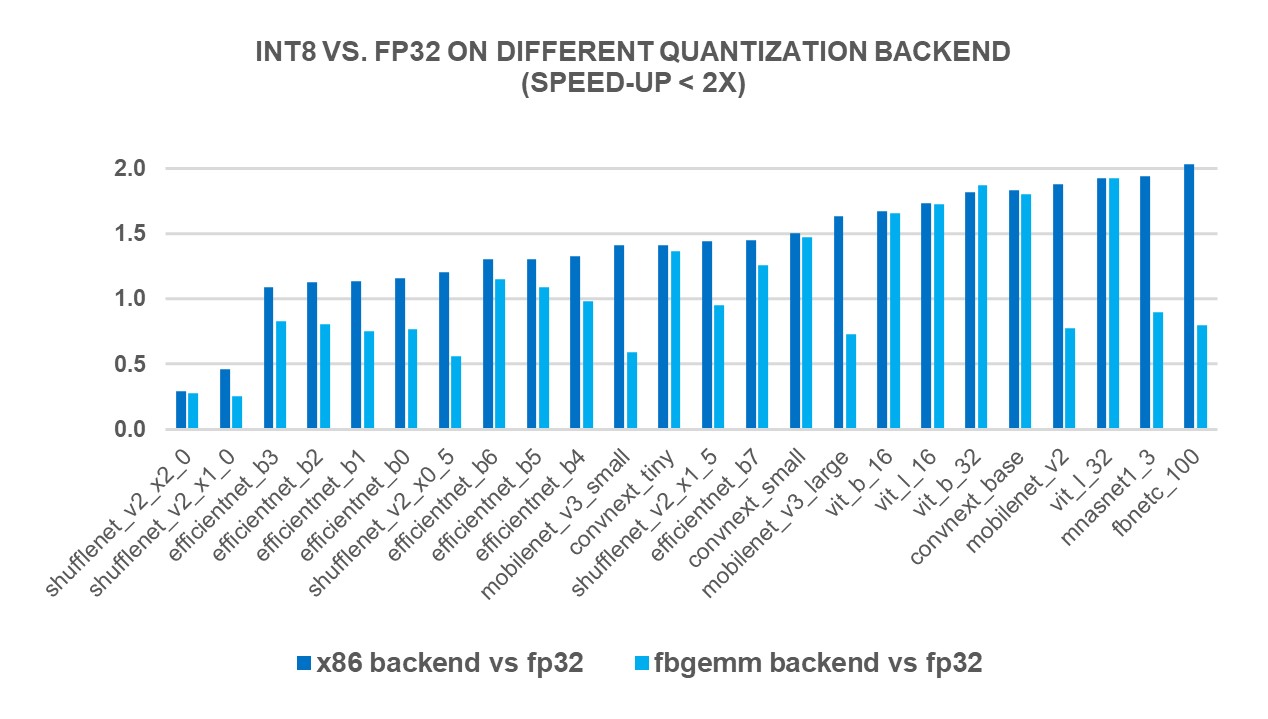
그림 1: x86 백엔드에서 2배 미만 성능 향상 모델1 / Figure 1: Models with less than 2x performance boost with x86 backend1
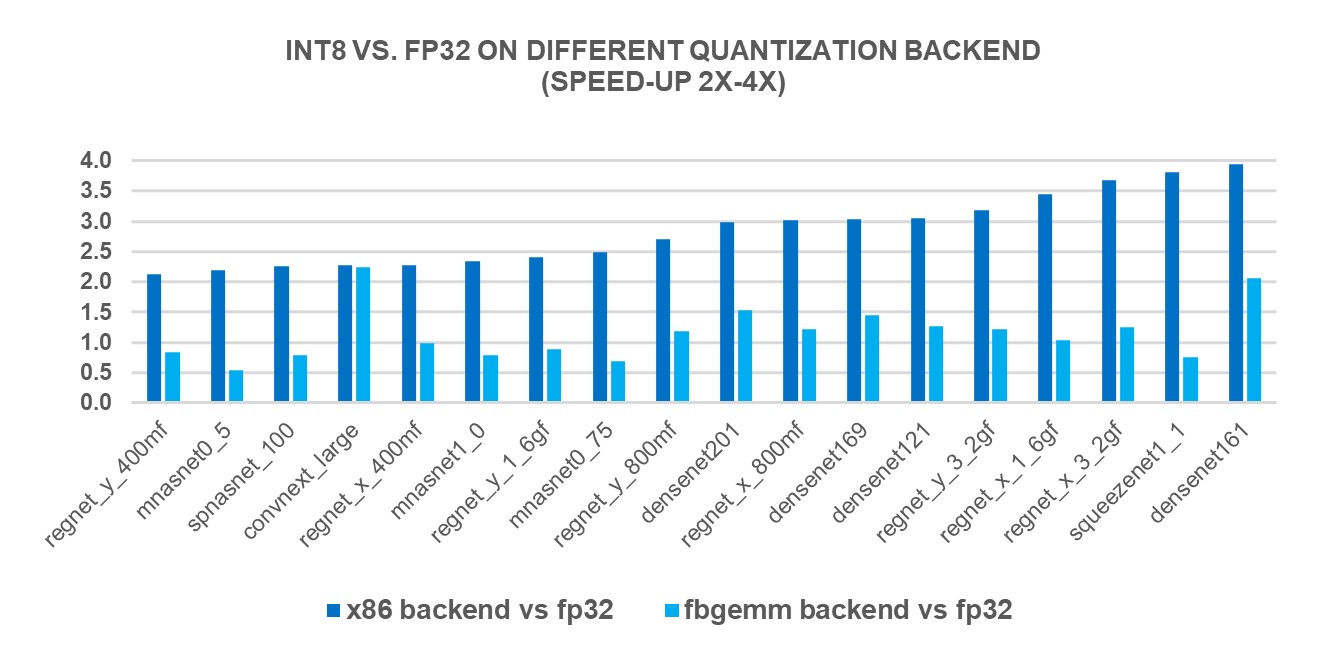
그림 2: x86 백엔드에서 2-4배 성능 향상 모델1 / Figure 2: Models with 2x-4x performance boost with x86 backend1
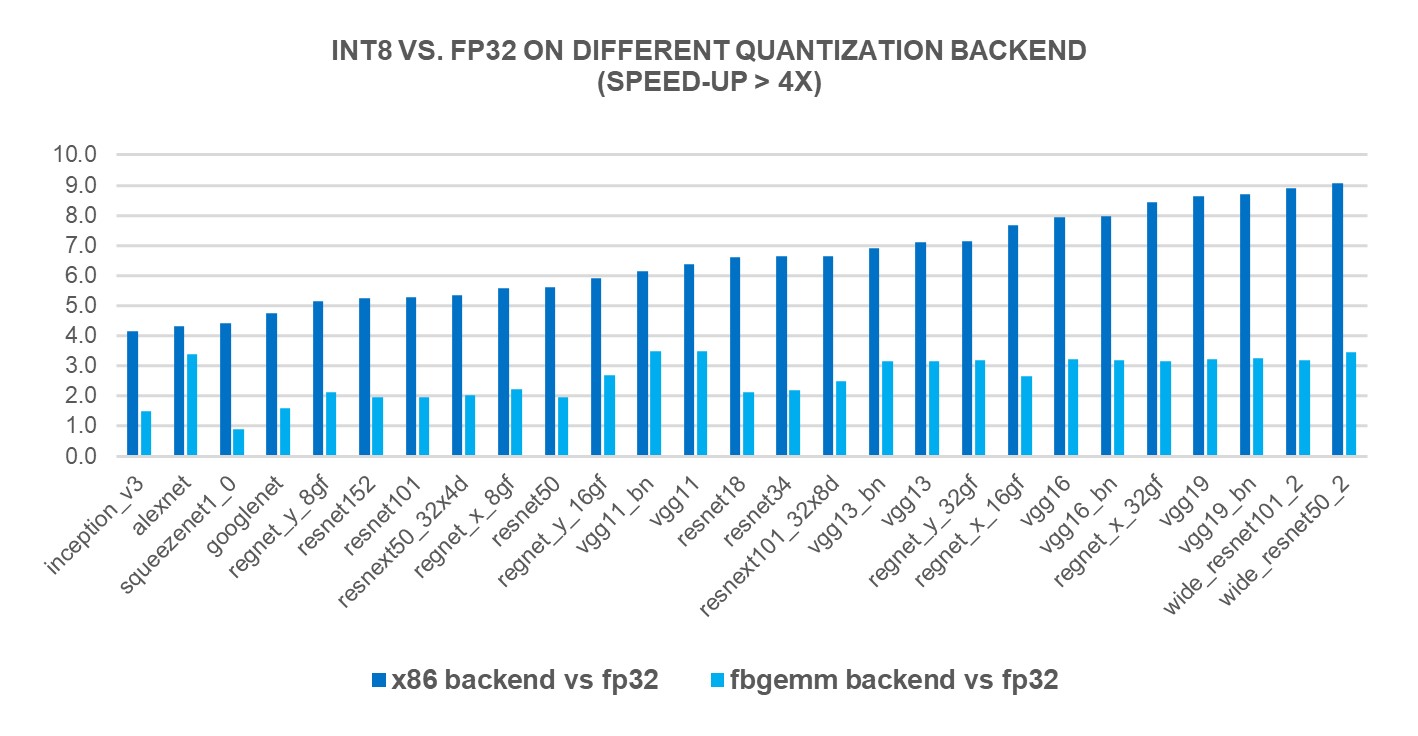
그림 3: x86 백엔드에서 4배 이상의 성능 향상 모델1 / Figure 3: Models with larger than 4x performance boost with x86 backend1
x86 백엔드 사용법 / Usage of x86 Backend
2.0에서는 기본적으로 x86 플랫폼 사용자는 x86 양자화 백엔드를 사용하며 기본 백엔드를 사용할 때는 프로그램 변경 없이도 동작합니다. 또는 사용자가 x86를 양자화 백엔드로 명시적(explitcit)으로 지정할 수 있습니다.
아래는 x86 양자화 백엔드를 사용한 PyTorch 정적 학습-후(post-training) 양자화 예제 코드입니다.
By default in 2.0, users on x86 platforms will use the x86 quantization backend and their PyTorch programs will remain unchanged when using the default backend. Alternatively, users can specify x86 as the quantization backend explicitly.
Below is an example code snippet of PyTorch static post-training quantization with x86 quantization backend.
import torch
from torch.ao.quantization import get_default_qconfig_mapping
from torch.quantization.quantize_fx import prepare_fx, convert_fx
qconfig_mapping = get_default_qconfig_mapping()
# 또는, 명시적으로 qengine을 명시합니다 / Or explicity specify the qengine
# qengine = 'x86'
# torch.backends.quantized.engine = qengine
# qconfig_mapping = get_default_qconfig_mapping(qengine)
model_fp32 = MyModel().eval()
x = torch.randn((1, 3, 224, 224), dtype=torch.float)
x = x.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
# qconfig_mapping과 백엔드 설정에 따라 관찰자(observer)를 삽입합니다
# Insert observers according to qconfig and backend config
prepared_model = prepare_fx(model_fp32, qconfig_mapping, example_inputs=x)
# 캘리브레이션 코드는 표시하지 않음 / Calibration code not shown
# 양자화된 모델로 변환 / Convert to quantized model
quantized_model = convert_fx(prepared_model)
x86 백엔드의 기술적 세부 사항 / Technical Details of x86 Backend
합성곱(convolution) 또는 행렬곱(matrix multiplication) 연산을 실행하기 위해서 oneDNN 또는 FBGEMM 성능 라이브러리 중 어떤 것을 호출할지 결정하기 위한 디스패치 규칙(dispatching rule)을 벤치마킹했던 모델들의 성능에 따라 휴리스틱하게 고안하였습니다. 이 규칙은 연산의 종류, 형태, CPU 아키텍처 정보 등을 고려하여 결정합니다. 자세한 로직은 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 더 많은 설계 및 기술적 논의는 RFC 문서(Request for Comments)를 참조하십시오.
We devised heuristic dispatching rules according to the performance numbers from the models we benchmarked to decide whether to invoke oneDNN or FBGEMM performance library to execute the convolution or matrix multiplication operations. The rules are a combination of operation kinds, shapes, CPU architecture information, etc. Detailed logic is available here. For more design and technical discussion, please refer to the Request for Comments.
새로운 양자화 경로, PyTorch 2.0 익스포트의 다음 단계 / Next Steps With a New Quantization Path PyTorch 2.0 Export
아직 확정되지는 않았지만, 새로운 양자화 경로인 파이토치 2.0 익스포트(PT2E; PyTorch 2.0 Export)가 현재 초기 설계 및 PoC 단계에 있으며, 향후 FX 양자화 경로를 대체할 것입니다. 이는 TorchDynamo Export라는 PyTorch 2.0에서 도입한 FX 그래프 캡쳐 기능을 기반으로 구축되었으며, 이 그래프는 양자화되어 다양한 백엔드들로 나눠(lowered)집니다. PyTorch의 새로운 DL 컴파일러인 TorchInductor는 x86 CPU에서 의미있는 FP32 추론 속도 향상을 보여주었으며, PT2E의 양자화 백엔드 중 하나로 만들기 위해 작업 중입니다. 이러한 새로운 경로가 다양한 계층(level)에서의 융합 가능성을 증대시켜 INT8 추론 성능을 더욱 향상시킬 것을 기대합니다.
Although still far from finalized, a new quantization path, PyTorch 2.0 Export (PT2E), is in early design and PoC stage. The new approach is slated to replace the FX quantization path in the future. It is built upon the capabilities of TorchDynamo Export, a feature introduced in the PyTorch 2.0 release for FX graph capturing. This graph is then quantized and lowered to different backends. TorchInductor, the new DL compiler of PyTorch, has shown promising results in terms of FP32 inference speedup on x86 CPU. We are working actively to enable it as one of the quantization backends of PT2E. We believe the new path will lead to further improvements in INT8 inference performance due to more flexibility of fusion at different levels.
결론 / Conclusion
PyTorch 2.0 출시 시 도입된 x86 백엔드는 x86 CPU 플랫폼에서 놀라운 INT8 추론 속도의 향상을 보였습니다. 기존 FBGEMM 백엔드와 비교하여 1.43배의 속도 향상을 보이면서도 하위 호환성 또한 유지합니다. 이러한 성능 향상으로 최종 사용자는 프로그램을 약간 또는 전혀 수정하지 않고도 성능 향상을 누릴 수 있게 되었습니다. 또한, 현재 개발 중인 새로운 양자화 경로인 PT2E는 미래에 더 많은 가능성을 제공할 수 있을 것으로 기대합니다.
The x86 backend introduced in PyTorch 2.0 release has demonstrated a remarkable improvement in INT8 inference speed on x86 CPU platforms. It offers a 1.43X speedup compared to the original FBGEMM backend while maintaining backward compatibility. This enhancement can benefit end users with minimal or no modifications to their programs. Furthermore, a new quantization path, PT2E, is currently in development and is expected to provide even more possibilities in the future.
감사의 글 / Acknowledgement
Nikita Shulga, Vasiliy Kuznetsov, Supriya Rao 및 Jongsoo Park에게 특별히 감사드립니다. 이들과 함께 PyTorch CPU 생태계를 개선하기 위한 발걸음을 내딛을 수 있었습니다.
Special thanks to Nikita Shulga, Vasiliy Kuznetsov, Supriya Rao, and Jongsoo Park. Together, we made one more step forward on the path of improving the PyTorch CPU ecosystem.
실험 구성 / Configuration
-
AWS EC2 r7iz.metal-16xl instance (Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6455B, 32-core/64-thread, Turbo Boost On, Hyper-Threading On, Memory: 8x64GB, Storage: 192GB); OS: Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS; Kernel: 5.15.0-1028-aws; Batch Size: 1; Core per Instance: 4; PyTorch 2.0 RC3; TorchVision 0.15.0+cpu, 인텔이 2023년 3월 7일에 실험. 공개된 모든 보안 업데이트를 반영하지 않았을 수 있음(May not reflect all publicly available security updates). ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5 ↩6
더 궁금하시거나 나누고 싶은 이야기가 있으신가요? 파이토치 한국어 커뮤니티에 참여해주세요!