이 글은 PyTorch 공식 블로그의 글을 번역한 것입니다. 번역 글은 원문을 함께 표시합니다. 원문을 읽으시려면 여기를 클릭하세요. (This article is a Korean translation of the original post on the PyTorch official blog. Below translation includes the original text. To read the original post, click here.)
요약: 안드레이 카파시(Andrej Karpathy)가 GPT 모델을 컴팩트한 오픈소스로 구현한 nanoGPT를 예제로, 가속화된 파이토치 2.0 트랜스포머와 새로 도입된 torch.compile() 메서드를 사용하여 대규모 언어 모델을 가속하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 가속화된 PT2 트랜스포머와 함께 도입된 새로운 스케일드 닷 프로덕트 어텐션 연산자(scaled dot product attention operator)를 사용하여 플래시-어텐션(flash_attention) 커스텀 커널을 선택하고 배치당 훈련 시간을 ~143ms/배치 기준에서 ~113ms/배치로 단축(Nvidia A100 GPU로 측정)했습니다. 또한 SDPA 연산자를 사용한 향상된 구현으로 수치 안정성이 향상되었습니다. 마지막으로, 플래시 주의와 결합된 패딩 입력을 사용하여 추가 최적화를 달성하면 배치당 ~87ms로 개선됩니다.
TL;DR. We show how to use Accelerated PyTorch 2.0 Transformers and the newly introduced
torch.compile()method to accelerate Large Language Models on the example of nanoGPT, a compact open-source implementation of the GPT model from Andrej Karpathy. Using the new scaled dot product attention operator introduced with Accelerated PT2 Transformers, we select the flash_attention custom kernel and achieve faster training time per batch (measured with Nvidia A100 GPUs), going from a ~143ms/batch baseline to ~113 ms/batch. In addition, the enhanced implementation using the SDPA operator offers better numerical stability. Finally, further optimizations are achieved using padded inputs, which when combined with flash attention lead to ~87ms/batch.
최근 일상 생활에서 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)과 생성형 AI가 기하급수적으로 채택되고 있습니다. 이렇게 계속 성장하는 모델과 밀접하게 연관되어 있는 것은 시간과 하드웨어 활용도 측면에서 계속 증가하는 학습 비용입니다. PyTorch 팀은 (이전에는 “Better Transformer”로 알려진) Accelerated PyTorch 2 Transformers와 PyTorch 2.0의 JIT 컴파일을 통해 이러한 문제를 정면으로 해결해 왔습니다.
Recent times have seen exponential adoption of large language models (LLMs) and Generative AI in everyday life. Tightly coupled with these ever-growing models is the ever-growing training cost - in terms of both time and hardware utilization. The PyTorch team has tackled these challenges head on with Accelerated PyTorch 2 Transformers (previously known as “Better Transformer”) and JIT Compilation in PyTorch 2.0.
이 블로그 게시물에서는 트랜스포머 모델에서 중요한 계층인 스케일드 도트 프로덕트 어텐션(scaled dot product attention)이라고도 하는 SDPA의 커스텀 커널 구현을 활용하여 얻은 트레이닝 최적화에 대해 살펴봅니다. SDPA용 커스텀 커널은 여러 개의 개별적인 순차 연산을 전역적으로 최적화된 하나의 커널로 대체하여 많은 양의 중간 CUDA 메모리를 할당하지 않도록 합니다. 이 접근 방식은 메모리 대역폭 병목 현상을 줄여 SDPA의 계산 성능을 높이고, 메모리 풋프린트를 줄여 더 큰 배치 크기를 지원하며, 마지막으로 입력 텐서를 사전 스케일링하여 수치 안정성을 높이는 등 다양한 이점을 제공합니다. 이러한 최적화는 Andrej Karpathy의 GPT 오픈소스 구현인 nanoGPT에서 시연되었습니다.
In this blog post, we explore training optimizations gained by utilizing custom kernel implementations of SDPA - also known as scaled dot product attention - a critical layer in transformer models. The custom kernel for SDPA replaces several discrete sequential operations with one globally optimized kernel which avoids allocating a large amount of intermediate CUDA memory. This approach offers a number of advantages, including but not limited to: higher performance computation of SDPA by reducing memory bandwidth bottleneck, reduced memory footprint to support larger batch sizes, and finally added numerical stability by prescaling input tensors. These optimizations are demonstrated on nanoGPT, an open-source implementation of GPT from Andrej Karpathy.
배경 / BACKGROUND
스케일드 도트 프로덕트 어텐션(scaled dot product attention)은 “Attention is All You Need”에서 소개한 바와 같이 멀티헤드 어텐션의 기본 구성 요소이며, LLM 및 생성형 AI 모델에 광범위하게 적용되고 있습니다.
Scaled dot product attention is the fundamental building block of multihead attention, as introduced in “Attention is All You Need”, and has a wide range of applications in LLM and Generative AI models.
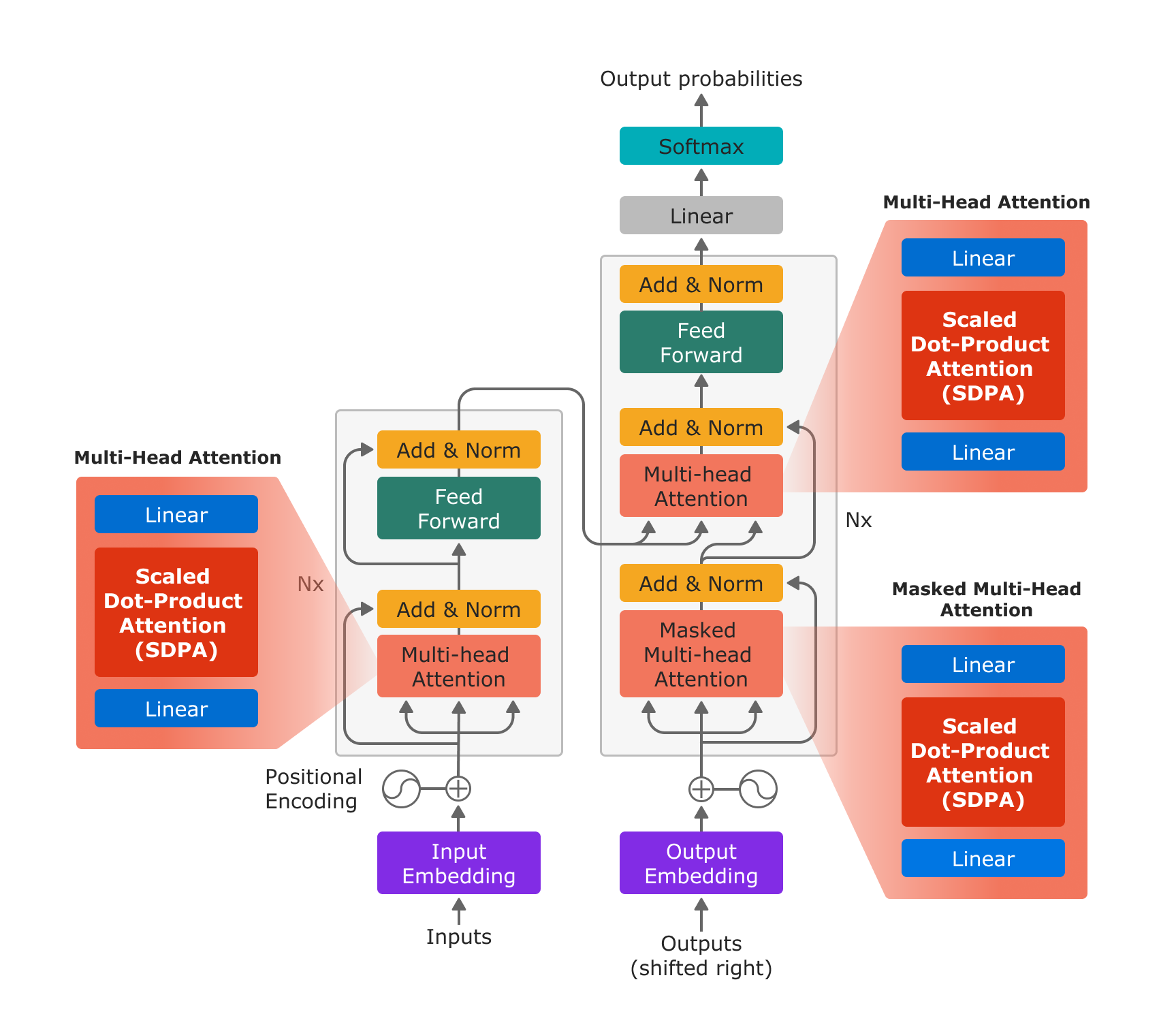
그림 1: “Attention is All You Need”에 기반한 트랜스포머 모델 아키텍처. 새로운 파이토치 SDPA 연산자를 사용하면 in-projection을 위한 선형 레이어, SDPA 연산자, out-projection을 위한 선형 레이어로 멀티 헤드 어텐션이 효율적으로 구현됩니다.
Figure 1: The Transformer model architecture based on “Attention is All You Need”. With the new PyTorch SDPA operator, Multi-Head Attention is efficiently implemented by a linear layer for the in-projection, the SDPA operator, and a linear layer for the out-projection.
새로운 scaled_dot_product_attention 연산자를 사용하면 선형 레이어를 사용한 in-projection, SDPA, 선형 레이어를 사용한 out-projection의 3단계만으로 멀티헤드 어텐션 기능을 구현할 수 있습니다.
With the new scaled_dot_product_attention operator, multihead attention can be implemented in just 3 steps: in projection with a linear layer, SDPA, and out projection with a linear layer.
# in_projection의 변수 설명:
# In Projection variable descriptions:
# q,k,v = Query, Key, Value tensors
# bsz = batch size
# num_heads = Numner of heads for Multihead Attention
# tgt_len = Target length
# src_len = Source Length
# head_dim: Head Dimension
q, k, v = _in_projection(query, key, value, q_proj_weight, k_proj_weight, v_proj_weight, b_q, b_k, b_v)
q = q.view(bsz, num_heads, tgt_len, head_dim)
k = k.view(bsz, num_heads, src_len, head_dim)
v = v.view(bsz, num_heads, src_len, head_dim)
# 스케일드 도트 프로덕트 어텐션 / Scaled Dot Product Attention
attn_output = scaled_dot_product_attention(q, k, v, attn_mask, dropout_p, is_causal)
# Out Projection
attn_output = attn_output.permute(2, 0, 1, 3).contiguous().view(bsz * tgt_len, embed_dim)
attn_output = linear(attn_output, out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias)
attn_output = attn_output.view(tgt_len, bsz, attn_output.size(1))
PyTorch 2는 특정 요구사항에 따라 특정 사용 사례에 최적화된 여러 가지 커널을 지원합니다. 커널 선택기는 특정 입력 매개변수 조합에 가장 적합한 커널을 선택합니다. 특정 입력 매개변수 조합에 최적화된 “사용자 지정 커널”을 찾을 수 없는 경우, 커널 선택기는 모든 입력 조합을 처리할 수 있는 일반 커널을 선택합니다.
PyTorch 2. supports multiple different kernels optimized for specific use cases, with specific requirements. A kernel picker picks the best kernel for a particular combination of input parameters. If no optimized “custom kernel” for a particular combination of input parameters can be identified, the kernel picker selects a general kernel that can handle all input combinations.
향후 릴리스에서 이 연산자 집합이 확장될 수 있지만, PyTorch 2.0에서는 SDPA 연산자를 위한 3가지 구현을 포함하고 있습니다:
While future releases may extend this set of operators, PyTorch 2.0 launches with 3 implementations for the SDPA operator:
- SDPA의 수학 방정식을
sdpa_math()함수에서 구현하는 일반 커널.- A generic kernel which implements the mathematical equation of SDPA in the function
sdpa_math()- SM80 컴퓨팅 아키텍처(A100)에서 16비트 부동소수점 데이터 유형으로 SDPA 평가를 지원하는 논문 “Flash Attention“에 기반하여 최적화된 커널.
- An optimized kernel based on the paper “Flash Attention”, which supports evaluation of SDPA with 16 bit floating point data types on compute architecture SM80 (A100).
- “Self-Attention Does Not Need $O(n^2)$ Memory“논문에 기반하는, 더 광범위한 아키텍처(SM40 이상)에서 32비트 및 16비트 부동 소수점 데이터 유형을 모두 지원하는 xFormer로 구현된 최적화된 커널입니다. 이 블로그 게시물에서는 이 커널을
mem_efficient커널이라고 부릅니다.- An optimized kernel based on the paper “Self-Attention Does Not Need $O(n^2)$ Memory” and implemented in xFormer, which supports both 32 and 16 bit floating data types on a wider range of architectures (SM40 and later). This blog post refers to this kernel as the
mem_efficientkernel.
최적화된 두 커널(위에 나열된 두 번째와 세 번째)은 모두 키 패딩 마스크를 지원하며 지원되는 어텐션 마스크를 인과 어텐션(causal attention)으로 제한한다는 점에 유의하세요. 현재 가속화된 PyTorch 2.0 트랜스포머는 인과 관계 마스크가 is_causal boolean값을 사용하여 지정된 경우에만 지원합니다. 마스크를 지정하면 제공된 마스크의 내용을 분석하여 인과 관계 마스크인지 판단하는 데 너무 많은 비용이 들기 때문에 범용 커널이 선택됩니다. 각 커널에 대한 제약 조건에 대한 자세한 설명은 가속화된 PT2 트랜스포머 블로그에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
Note that both optimized kernels (two and three listed above), support a key padding mask and limit the supported attention mask to causal attention. Accelerated PyTorch 2.0 Transformers today only support the causal mask when it is specified using the
is_causalboolean. When a mask is specified, the general-purpose kernel will be selected because it is too expensive to analyze the contents of a provided mask to determine if it is the causal mask. Additional explanations on the constraints for each kernel can be found in the Accelerated PT2 Transformer blog.
NANOGPT로 가속화된 트랜스포머 활성화하기 / ENABLING ACCELERATED TRANSFORMERS WITH NANOGPT
SDPA 연산자는 GPT 모델의 핵심 구성 요소이기 때문에 오픈소스 nanoGPT 모델이 구현의 용이성과 PyTorch 2.0의 가속화된 트랜스포머의 이점을 모두 입증할 수 있는 훌륭한 후보라고 판단했습니다. 다음은 nanoGPT에서 가속화된 트랜스포머가 활성화된 정확한 프로세스를 보여줍니다.
The SDPA operator being a critical component of the GPT model, we identified the open source nanoGPT model as an excellent candidate for both demonstrating the ease of implementation and benefits of PyTorch 2.0’s Accelerated Transformers. The following demonstrates the exact process by which Accelerated Transformers was enabled on nanoGPT.
이 프로세스는 크게 기존 SDPA 구현을 functional.py에서 새로 추가된 F.scaled_dot_product_attention 연산자로 대체하는 것을 중심으로 진행됩니다. 이 프로세스는 다른 많은 LLM에서 이 연산자를 활성화하도록 쉽게 조정할 수 있습니다. 또는 사용자가 F.multi_head_attention_forward()를 호출하거나 해당되는 경우 nn.MultiHeadAttention 모듈을 직접 활용할 수 있습니다. 다음 코드 스니펫은 Karpathy의 nanoGPT 저장소에서 가져온 것입니다.
This process largely revolves around replacing the existing SDPA implementation with the newly added F.scaled_dot_product_attention operator from functional.py. This process can be easily adapted to enable the operator in many other LLMs. Alternatively, users can instead choose to call F.multi_head_attention_forward() or utilize the nn.MultiHeadAttention module directly where applicable. The following code snippets are adapted from Karpathy’s nanoGPT repository.
1단계: 기존 SDPA 구현 식별하기 / Step 1: Identify the existing SDPA implementation
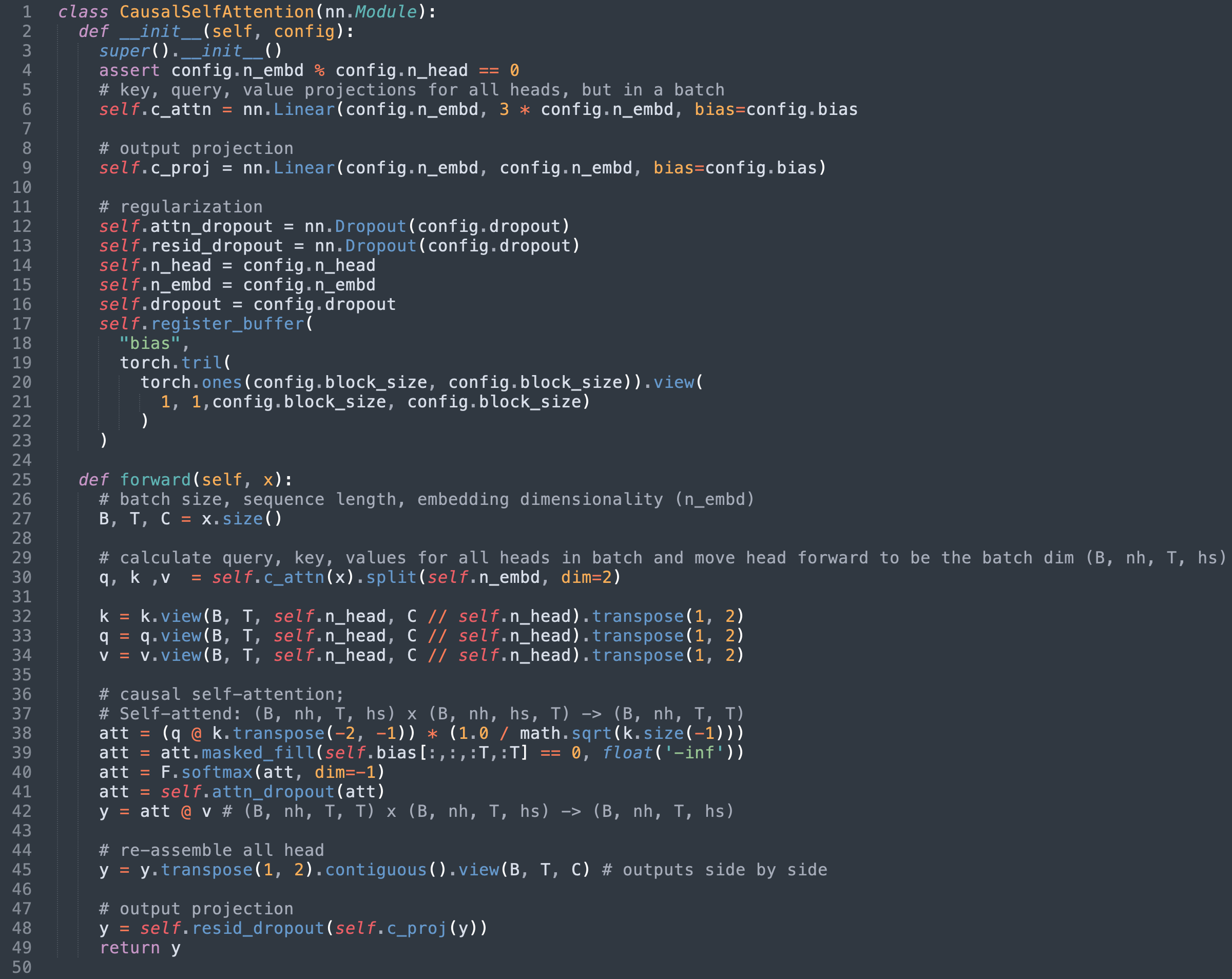
nanoGPT의 경우, SDPA는 모델의 CausalSelfAttention 클래스에서 구현됩니다. 이 포스팅을 작성할 당시의 원본 구현을 아래에 적용했습니다.
In the case of nanoGPT, SDPA is implemented in the model’s CausalSelfAttention class. The original implementation at time of writing is adapted below for this post.
2단계: Torch의 scaled_dot_product_attention으로 바꾸기 / Step 2: Replace with Torch’s scaled_dot_product_attention
이 지점에서 다음 사항들을 확인할 수 있습니다:
At this point we can note the following:
- 36~42줄은 우리가 대체할 SDPA의 수학적 구현을 정의합니다.
- 39줄에 적용된 마스크는 scaled_dot_product_attention의
is_causal플래그를 사용하기 때문에 더 이상 필요하지 않습니다. - 41번 라인에 사용된 드롭아웃 레이어도 이제 불필요합니다.
- Lines 36 - 42 define the mathematical implementation of SDPA which we are replacing
- The mask applied on line 39 is no longer relevant since we are using scaled_dot_product_attention’s
is_causalflag. - The dropout layer used in line 41 is also now unnecessary.
SDPA 구현을 파이토치의 scaled_dot_product_attention으로 바꾸고 이제 중복 코드를 제거하면 다음과 같은 구현이 생성됩니다.
Swapping out the SDPA implementation for torch’s scaled_dot_product_attention and removing the now redundant code yields the following implementation.
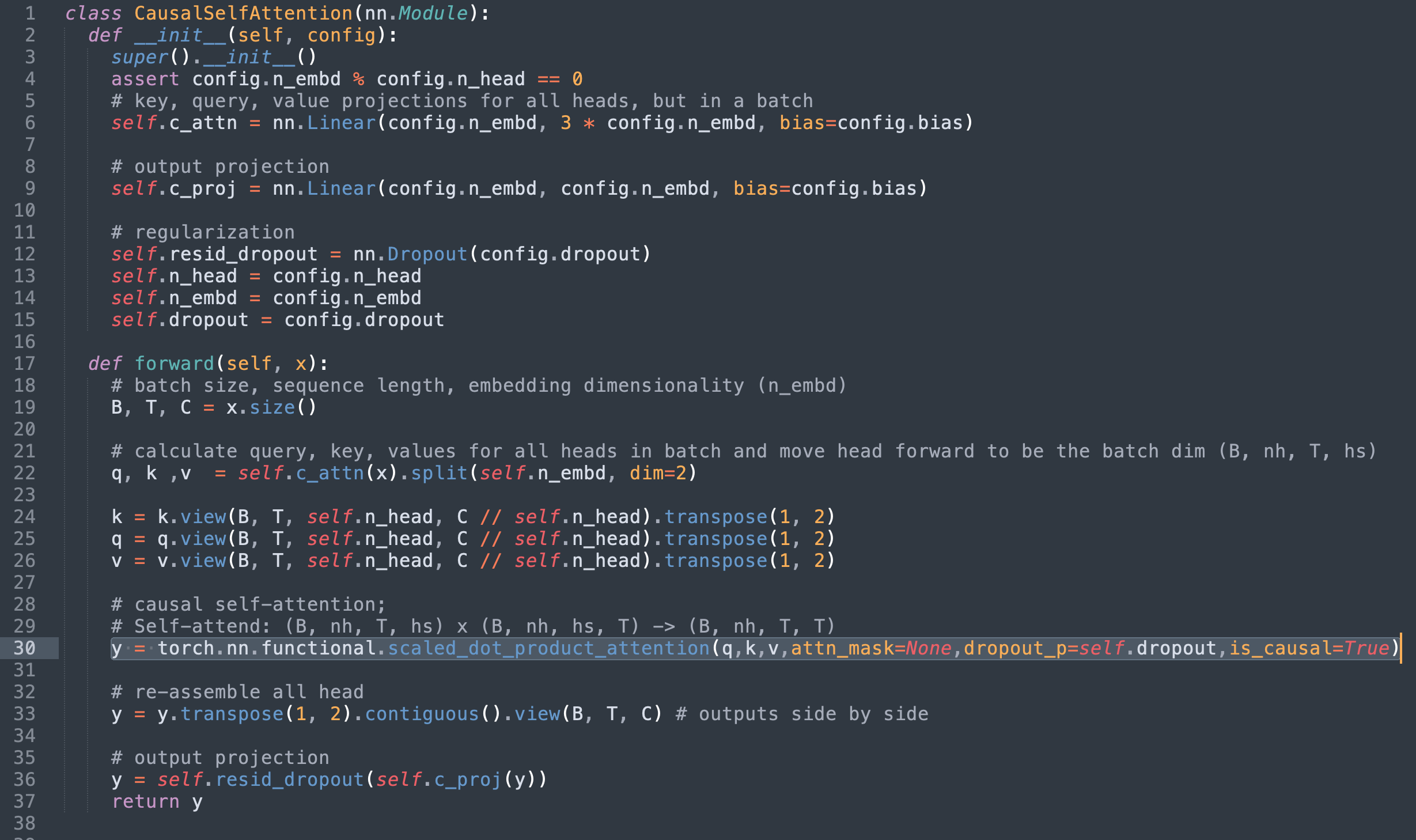
또한 원본 마스크를 attn_mask 필드에 전달할 수도 있지만, 앞서 언급한 커널 제약 조건으로 인해 구현이 일반 sdpa_math 커널만 지원하도록 제한됩니다.
Alternatively, the original mask can be passed into the
attn_maskfield however due to the mentioned kernel constraints that would limit the implementation to only support the genericsdpa_mathkernel.
3단계 (보너스): 패딩으로 더 빨라진 matmul / Step 3 (Bonus): Faster matmuls with padding
SDPA를 통한 성능 개선 외에도, 분석 결과 부수적인 성과도 얻을 수 있었습니다. Andrej의 말을 빌리자면, “지금까지 nanoGPT에 대한 가장 극적인 최적화(~25% 속도 향상)는 단순히 어휘 크기를 50,257에서 50,304(64의 근사 배수)로 늘린 것뿐입니다.”라고 합니다.
On top of the performance improvements from SDPA, our analysis yielded a nice ancillary win. In Andrej’s words “The most dramatic optimization to nanoGPT so far (~25% speedup) is to simply increase the vocab size from 50257 to 50304 (nearest multiple of 64).”

어휘 크기는 GPT의 출력 레이어에서 matmul의 크기를 결정하는데, 이 크기가 너무 커서 전체 학습 루프에서 대부분의 시간을 차지하고 있었습니다! 우리는 A100 GPU에서 달성할 수 있는 최대 처리량에 훨씬 못 미치는 성능을 보이고 있다는 사실을 발견했고, NVIDIA의 matmul 문서를 통해 64-요소 정렬이 더 나은 결과를 얻을 수 있을 것이라고 추측했습니다. 실제로 이렇게 matmul을 패딩하면 거의 3배의 속도 향상을 달성할 수 있습니다! 근본적인 원인은 정렬되지 않은 메모리 액세스가 효율성을 크게 떨어뜨리기 때문입니다. 더 자세한 분석은 이 트위터 스레드에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
The vocab size determines the dimensions of matmuls in the output layer of GPT, and these are so large that they were taking a majority of the time for the entire training loop! We discovered that they were achieving performance significantly below the peak throughput achievable on the A100 GPU, and guessed from NVIDIA’s matmul documentation that 64-element alignment would yield better results. Indeed, padding these matmuls achieves nearly a 3x speedup! The underlying cause is that unaligned memory accesses significantly reduce efficiency. A deeper analysis can be found in this Twitter thread.
이 최적화를 통해 훈련 시간을 배치당 최대 113밀리초(플래시 어텐션 사용)에서 최대 87밀리초로 더욱 단축할 수 있었습니다.
With this optimization we were able to further reduce training time from ~113 ms (using flash attention) to ~87 ms per batch.
결과 / RESULTS
아래 그림은 파이토치 커스텀 커널을 사용하여 얻은 성능을 보여줍니다. 정확한 수치는 다음과 같습니다:
The figure below demonstrates the performance gained using Pytorch custom kernels. Here are the exact figures:
- baseline (nanoGPT implementation): ~143ms
- sdpa_math (generic): ~134ms (6.71% faster)
mem_efficientkernel: ~119ms (20.16% faster)flash_attentionkernel: ~113ms (26.54% faster)- flash_attention + padded vocab: ~87ms (64.37% faster)
모든 코드는 80GB HBM [A100 SXM4 80GB]이 장착된 8 x NVIDIA Corporation A100 서버에서 실행되었으며, 이 실험을 위해 드롭아웃은 0으로 설정했습니다.
All code was run on an 8 x NVIDIA Corporation A100 server with 80 GB HBM [A100 SXM4 80GB], and for the purpose of this experiment dropout was set to 0.
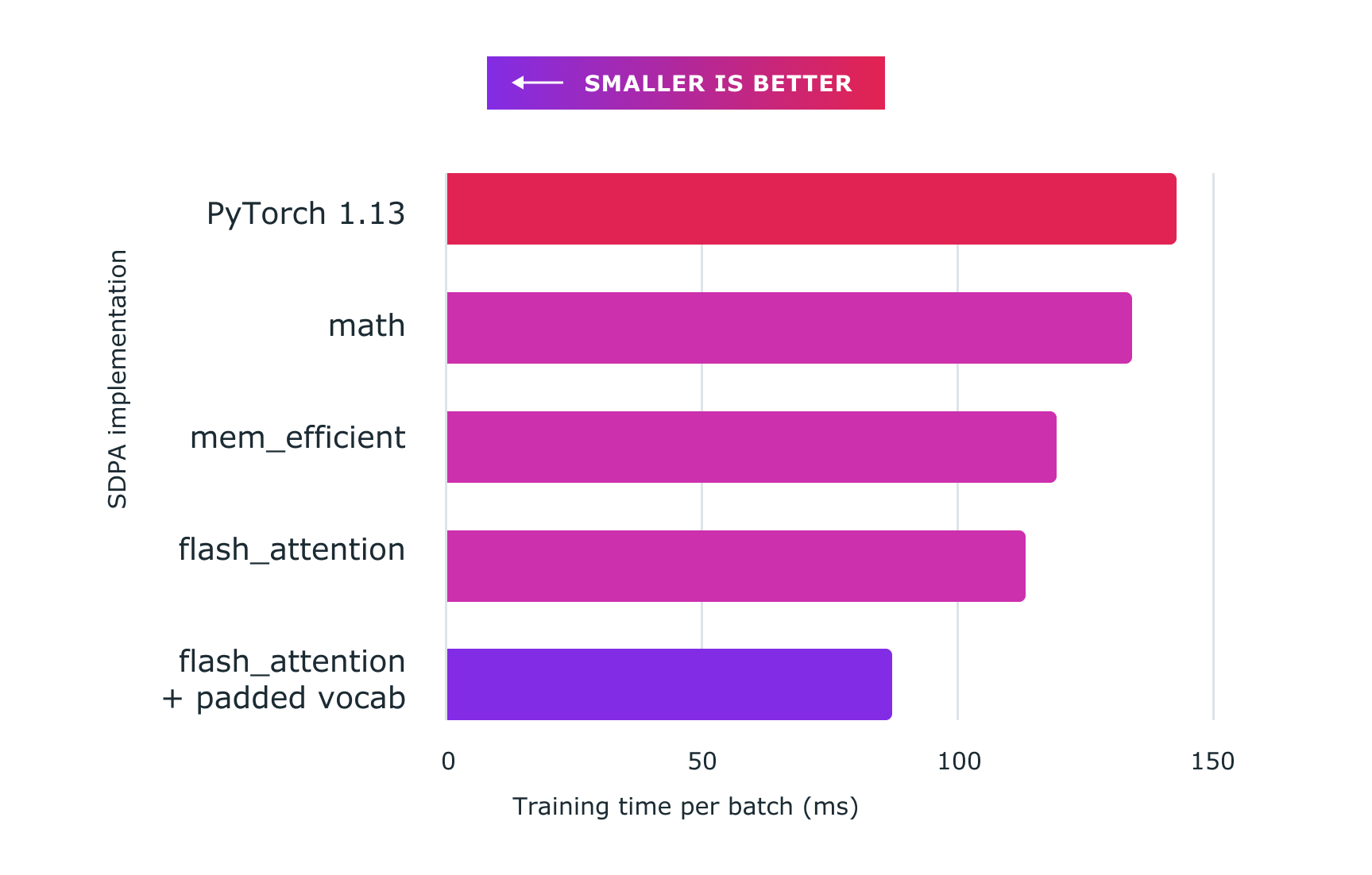
그림 2: 커스텀 커널 및 torch.compile과 함께 스케일드 도트 프로덕트 어텐션을 사용하면 여기에 표시된 nanoGPT와 같은 대규모 언어 모델을 훈련하는 데 상당한 속도 향상을 제공합니다. *
Figure 2: Using scaled dot product attention with custom kernels and torch.compile delivers significant speedups for training large language models, such as for nanoGPT shown here.
수치 모델 안정성 향상 / ENHANCING NUMERICAL MODEL STABILITY
파이토치 구현은 더 빠를 뿐만 아니라, 많은 실행 시나리오에서 정밀도 손실을 방지하여 수치 안정성이 향상됩니다. 여기에 더 좋은 설명이 있지만, 기본적으로 PyTorch 구현은 곱하기 전에 쿼리 및 키 행렬을 스케일링하므로 더 안정적이고 정밀도 손실을 피할 수 있다고 합니다. SDPA의 병합된 커스텀 커널 아키텍처로 인해 이러한 스케일링은 어텐션 결과 계산에 추가적인 오버헤드를 발생시키지 않습니다. 이에 비해 개별 계산 구성 요소에서 구현할 경우 추가 비용을 들여 별도의 사전 스케일링을 수행해야 합니다. 자세한 설명은 부록 A를 참조하세요.
In addition to being faster, PyTorch’s implementation offers increased numerical stability by avoiding loss of precision in many execution scenarios. There is a great explanation here, but essentially the PyTorch implementation scales the Query and Key matrices before multiplication, which is said to be more stable and avoid loss of precision. Because of the merged custom kernel architecture of SDPA, this scaling does not introduce additional overhead in the computation of the attention result. In comparison, an implementation from the individual computational components would require separate pre-scaling at additional cost. For an additional explanation, see Appendix A.
메모리 소비량 개선 / Improved Memory Consumption
토치 SDPA 커널 사용의 또 다른 큰 장점은 메모리 사용 공간을 줄여 더 큰 배치 크기를 활용할 수 있다는 점입니다. 다음 차트는 플래시 어텐션와 인과 어텐션의 기본 구현 모두에 대한 1시간 학습 후 최상의 검증 손실을 비교한 것입니다. 보시다시피, 기준 인과적 어텐션 구현으로 달성한 최대 배치 크기는 24개로 플래시 어텐션으로 달성한 최대 크기인 39개보다 훨씬 적습니다.
Yet another large advantage of using the torch SDPA kernels is the reduced memory footprint, which allows for the utilization of larger batch sizes. The following chart compares the best validation loss after one hour of training for both flash attention and the baseline implementations of causal attention. As can be seen, the maximum batch size achieved with the baseline causal attention implementation (on 8 x NVIDIA Corporation A100 server with 80 GB HBM) was 24, significantly less then the maximum achieved with flash attention, which was 39.
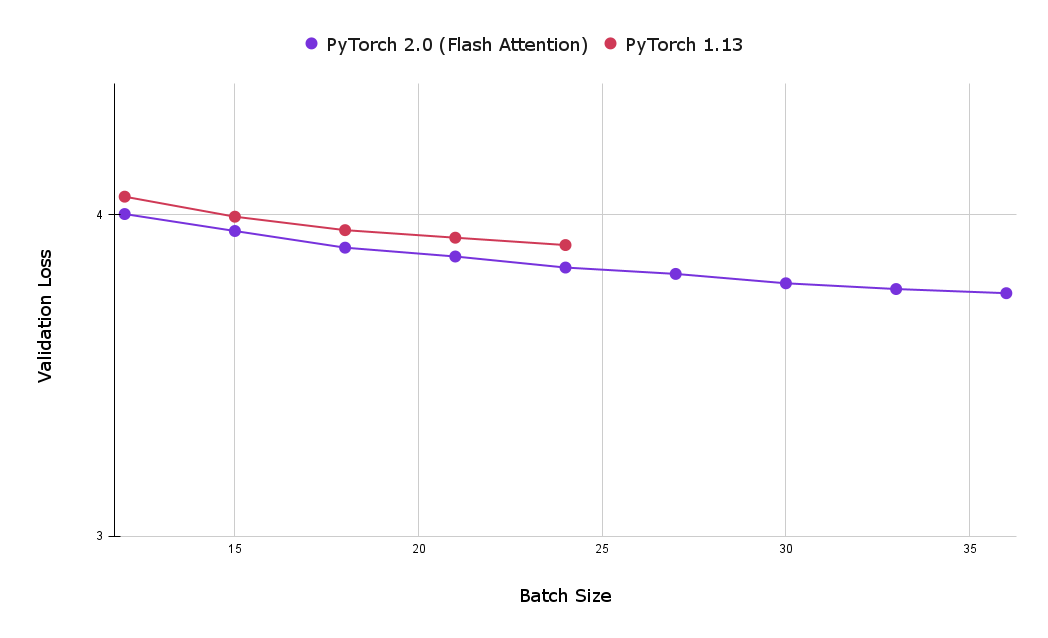
그림 3: 플래시 어텐션을 사용하면 더 큰 배치 크기를 사용할 수 있으므로 단 1시간의 학습 후에도 검증 손실을 줄일 수 있습니다(작을수록 좋음).
Figure 3: Using Flash Attention enables the usage of larger batch sizes, allowing users to achieve lower validation loss after one hour of training (smaller is better).
결론 / CONCLUSION
가속화된 PyTorch 2 트랜스포머는 최신 트랜스포머 모델의 트레이닝 및 프로덕션 배포를 경제적으로 수행할 수 있도록 설계되었으며 PyTorch 2.0 모델 JIT 컴파일과 통합되었습니다. 새로 도입된 PyTorch SDPA 연산자는 트랜스포머 모델 학습에 향상된 성능을 제공하며 특히 고비용의 대규모 언어 모델 학습에 유용합니다. 이 게시물에서는 예시적인 nanoGPT 모델에서 다음과 같은 여러 가지 최적화를 시연합니다.
Accelerated PyTorch 2 Transformers were designed to make the training and production deployment of state-of-the-art transformer models affordable and integrated with PyTorch 2.0 model JIT compilation. The newly introduced PyTorch SDPA operator provides improved performance for training Transformer models and is particularly valuable for the expensive Large Language Model training. In this post we demonstrate a number of optimizations on the exemplary nanoGPT model including:
- 일정한 배치 크기로 기준과 비교했을 때 26% 이상의 훈련 속도 향상
- 어휘 추가를 통한 추가 속도 향상으로 총 최적화가 기준 대비 약 64%에 달함.
- 추가적인 수치 안정성
- Over 26% training speedup, when compared against the baseline with constant batch size
- An additional speedup achieved with padded vocabulary, bringing the total optimization to approximately 64% compared to the baseline
- Additional numerical stability
부록 A: 어텐션 수치 안정성 분석 / APPENDIX A: ANALYZING ATTENTION NUMERIC STABILITY
이 섹션에서는 앞서 언급한 SDPA의 입력 벡터를 프리스케일링함으로써 얻을 수 있는 향상된 수치 안정성에 대해 자세히 설명합니다. 다음은 nanoGPT의 수학적 구현을 단순화한 버전의 SDPA입니다. 여기서 주목해야 할 점은 쿼리가 스케일링되지 않고 행렬 곱셈을 수행한다는 것입니다.
In this section we provide a more in depth explanation of the previously mentioned enhanced numerical stability which is gained by prescaling SDPA’s input vectors. The following is a simplified version of nanoGPT’s mathematical implementation of SDPA. The important thing to note here is that the query undergoes matrix multiplication without being scaled.
# nanoGPT implementation of SDPA
# notice q (our query vector) is not scaled !
att = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * (1.0 / math.sqrt(k.size(-1)))
att = att.masked_fill(self.bias[:,:,:T,:T] == 0, float('-inf'))
att = F.softmax(att, dim=-1)
# 드롭아웃이 0으로 설정되어 있으므로 구현에서 이 줄은 무시해도 됩니다
# Dropout is set to 0, so we can safely ignore this line in the implementation
# att = self.attn_dropout(att)
y_nanogpt = att @ v # (B, nh, T, T) x (B, nh, T, hs) -> (B, nh, T, hs)
다음은 토치의 scaled_dot_product_attention에서 이와 동등한 수학적 구현입니다.
The following is the equivalent mathematical implementation in torch’s
scaled_dot_product_attention.
# PyTorch implementation of SDPA
embed_size = q.size(-1)
scaling_factor = math.sqrt(math.sqrt(embed_size))
q = q / scaling_factor # notice q _is_ scaled here !
# same as above, but with scaling factor
att = q @ (k.transpose(-2, -1) / scaling_factor)
att = att.masked_fill(self.bias[:,:,:T,:T] == 0, float('-inf'))
att = F.softmax(att0, dim=-1)
# 드롭아웃이 0으로 설정되어 있으므로 구현에서 이 줄은 무시해도 됩니다
# Dropout is set to 0, so we can safely ignore this line in the implementation
# att = self.attn_dropout(att)
y_scale_before = att @ v
수학적으로는 두 접근 방식이 동일해야 하지만, 실험 결과, 실제로는 각 접근 방식에서 서로 다른 결과를 얻을 수 있었습니다.
Mathematically both approaches should be equivalent, however our experimentation shows that in practice we receive different results from each approach.
위의 접근법을 사용하여 y_scale_before는 scaled_dot_product_attention 메서드를 사용한 예상 결과와 일치하는 반면, y_nanogpt는 그렇지 않음을 확인했습니다.
Using the approach above, we verified
y_scale_beforematches the expected output from using thescaled_dot_product_attentionmethod whiley_nanogptdoes not.
동등성을 테스트하기 위해 torch.allclose 메서드를 사용했습니다. 더 자세히 확인해보겠습니다:
The
torch.allclosemethod was used to test equivalence. Specifically, we showed that:
y_sdpa = torch.nn.functional._scaled_dot_product_attention(
q,
k,
v,
attn_mask=self.bias[:,:,:T,:T] != 0,
dropout_p=0.0,
need_attn_weights=False,
is_causal=False,
)
torch.allclose(y_sdpa, y_nanogpt) # False, fp 문제를 나타냅니다. / False, indicating fp issues
torch.allclose(y_sdpa, y_scale_before) # 예상대로 True / True, as expected
부록 B: 실험 결과 재현하기 / APPENDIX B: REPRODUCING EXPERIMENT RESULTS
이러한 결과를 재현하고자 하는 연구자는 Andrej의 nanoGPT 저장소에서 다음 커밋(b3c17c6c6a363357623f223aaa4a8b1e89d0a465)으로 시작해야 합니다. 이 커밋은 배치당 속도 개선을 측정할 때 기준선으로 사용되었습니다. 배치 속도를 가장 크게 개선한 패딩 어휘 최적화가 포함된 결과를 보려면 다음 커밋 - 77e7e04c2657846ddf30c1ca2dd9f7cbb93ddeab을 사용하세요. 어느 커밋에서든 실험용 커널을 선택하려면 torch.backends API를 사용하면 간단합니다.
Researchers seeking to reproduce these results should start with the following commit from Andrej’s nanoGPT repository - b3c17c6c6a363357623f223aaa4a8b1e89d0a465. This commit was used as the baseline when measuring the per batch speed improvements. For results which include padded vocabulary optimizations (which yielded the most significant improvements to batch speed), use the following commit - 77e7e04c2657846ddf30c1ca2dd9f7cbb93ddeab. From either checkout, selecting kernels for experimentation is made trivial with the use of the torch.backends API.
컨텍스트 관리자를 통해 원하는 커널을 선택할 수 있습니다:
The desired kernel can be selected via a context manager:
with torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel (
enable_math = False,
enable_flash = False,
enable_mem_efficient = True
):
train(model)
이 주제와 관련하여 더 궁금하시거나 나누고 싶은 이야기가 있으신가요? 파이토치 한국어 커뮤니티에 참여해주세요!